Hello readers welcome to the new post. In this post, we will have a look at The Importance of Copper Pour in Empty Areas on PCBs. Copper pours are important for the design of printed circuit boards. It comes with filling empty areas on the PCB board with copper planes, which provides many benefits for electronic circuits. In this post, we will cover different parameters of f copper pour and its impact on board performance. Let's get started with Introduction to Copper Pour
Introduction to Copper Pour
When designing boards, engineers strive to enhance their functionality, reliability, and performance. The copper pour is a method that helps achieve these goals with the use of the empty areas on the board to enhance its overall performance. By filling these areas with copper planes, engineers effectively manage heat dissipation, decrease electromagnetic interference (EMI), and enhance signal integrity.
[adinserter block="3"]
What is Copper Pour on PCBs?
Copper pour defines the process of making large areas of continuous copper planes on the circuit board. These planes are attached to the ground or power plane and cover the empty spaces between components and traces. This pour is typically implemented on the internal layers of the board, although it can also be used on the outer layers.
Why is Copper Pour Important?
Enhancing Heat Dissipation
One of the main reasons for incorporating copper pour-in board design is its ability to enhance heat dissipation. The heat produced by active components can be efficiently conducted through the copper planes and distributed about the board. This avoids localized hotspots and makes sure of optimal operating temperatures for components, thereby enhancing their lifespan and reliability.
Reducing Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
Copper pour also helps to minimize electromagnetic interference within the PCB. The continuous copper planes work as shields, reducing the coupling of electromagnetic fields among traces and components. This decreases the chances of cross-talk, signal degradation, and unwanted noise, resulting in enhanced overall system performance.
Improving Signal Integrity
Another main advantage of the copper pour is its impact on signal integrity. By providing a less-impedance path, the copper planes help smooth signal transmission and decrease the effects of impedance mismatch. This is important for high-speed digital and analog circuits where maintaining signal integrity is required.
Wholesale PCBs SMT Stencil & PCBA Service Provider Special offer:$2 for 1-8 layer PCBs
Copper Pour Design Considerations
To make effective copper pour implementation, certain design considerations must be followed
The copper weight for the pour area is based on the certain needs of the board design. High copper weights can offer good heat dissipation and current-carrying capacity, but they can also increase manufacturing expenses and introduce etching challenges. It is necessary to balance these factors and choose a good copper weight that aligns with the design goals.
Clearance and Spacing
Clearance and spacing about the copper pour area are critical to avoid unintended shorts or signal interference. Proper clearances must be maintained between the copper pour and other components, and signal lines. and traces, Adhering to design guidelines and industry standards make sure reliable performance and prevents potential issues.
Shape and Placement
The shape and placement of the copper pour areas must be carefully considered to optimize the board performance. Irregular or poorly placed copper pour can cause uneven heat distribution or ineffective EMI shielding. Engineers must strive for a well-planned copper pour design that enhances benefits while minimizing potential failures
Split Planes
In some conditions, it can be necessary to split copper pour areas into many sections or planes. This is used for good control of current flow, decreased impedance, and improved isolation between different circuit sections. Accurate segmentation and partitioning methods should be used based on certain design requirements.
Benefits of Copper Pour
Thermal Management
These pour effectively spreads and dissipate heat in PCB, providing optimal operating temperatures for components. By reducing hotspots and maintaining a balanced thermal profile, copper pour increases the lifespan and reliability of electronic devices.
EMI Shielding
The continuous copper planes are shields, that reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) in the board. it provides improved signal quality, minimizes noise, and enhanced overall system performance.
Voltage Distribution
Copper pour helps in maintaining a consistent voltage distribution across the board It minimizes voltage loss and makes sure stable power delivery to components, like in areas with high current required
Signal Integrity Enhancement
By providing low-impedance paths, copper pour helps to improve signal integrity. It decreases signal reflections, , and crosstalk, attenuations, allowing for reliable data transmission and correct circuit function
Copper Pour Techniques
[adinserter block="5"]
Solid Copper Pour
In the solid copper pour process, the empty areas on the board are filled completely with a continuous copper plane. This offers maximum heat dissipation, EMI protection, and signal integrity enhancement. Though it can not be best for all designs due to cost and manufacturing constraints.
Hatched Copper Pour
The hatched copper pour methods involve making grid-like patterns within the copper pour area, leaving small gaps between copper traces. This process strikes a balance between heat dissipation and manufacturing considerations. It is used for effective copper pouring while reducing etching challenges and material expenses
Thermal Relief Pads
Thermal relief pads are copper connections employed to have isolation between surface-mount components and copper planes. These pads reduce heat transfer from the components to the copper pour, make sure proper soldering and prevent tombstoning issues.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Insufficient Copper Pour
Improper coverage of empty areas with copper pour can restrict the benefits it provides. Ineffective copper pour can cause inadequate heat dissipation, enhanced EMI, and compromised signal integrity.
Excessive Copper Pour
While, excessive copper pour causes over-consumption of copper material, high manufacturing costs, and potential manufacturing problems. It is necessary to make balance and optimize the copper pour based on the specific design requirements
Inadequate Clearance and Spacing
Neglecting good clearance and spacing around the copper pour areas can cause in shorts or interference with neighboring components or signal lines. Following design guidelines and performing proper checks can help to minimize such problems.
Inconsistent Copper Weight
Inconsistencies in the copper weight across the pour area can affect its performance. Uneven copper distribution can result in impedance variations, thermal imbalances, and compromised signal integrity.
Best Practices for Copper Pour
Follow Design Guidelines
Following the design guidelines and industry standards is important for successful copper pour implementation. These instructions provide recommendations on copper weights, spacing, clearances, and other parameters necessary for reliable and optimized board designs.
Optimize Copper Fill Areas
Accurate optimization of copper fill areas helps increase the advantages of copper pour while reducing any potential failure. Balancing thermal needs, EMI considerations, and signal integrity needs is compulsory for effective copper pour design.
Perform Design Rule Checks (DRC)
Conducting thorough design rule checks is important to find and rectify any potential problems related to copper pour. DRC instruments and simulations can validate the design and make sure compliance with design rules and features
Copper Pour in Different Applications
High-Speed PCBs
In high-speed PCBs, maintaining signal integrity is important. Copper pour reduces signal distortions, reflections, and crosstalk, making sure of reliable data transmission in high-frequency circuits.
Power Electronics
Power electronics produce significant heat. Copper pour helps in effective heat dissipation, provides reliable operation, and extends the lifespan of power devices and components.
RF and Wireless Communication
RF and wireless communication circuits need stringent control over signal quality and EMI. Copper pour reduces interference, signal losses, and noise, causing improved RF performance.
How Does Copper Pour Affect Crosstalk and EMI?
Copper pours on a PCB board can have both positive and negative effects on crosstalk and EMI. The impact of copper pours is based on their configuration and placement in relation to signal traces. Here's how copper pours can affect crosstalk and EMI explained
- Crosstalk Reduction: Copper pours can reduce crosstalk by working as a protective barrier between sensitive signal traces. By surrounding high-speed signal traces with copper pours, the electromagnetic fields produced by neighboring traces can be attenuated. it minimizes the coupling of signals between adjacent traces and reduces crosstalk.
- Ground Plane: These pours configured to a solid ground plane can offer a low-impedance return path for signals. This helps to minimize the loop area of high-speed signals, which in turn decreases the chances of crosstalk. Ground planes also help in maintaining a stable reference voltage and reduce ground bounce.
- Impedance Control: They can be used to control the characteristic impedance of transmission lines. By setting the width and placement of copper pours, we can fine-tune the impedance to match the required value. It helps to reduce signal reflections and enhances signal integrity, decreasing the potential for crosstalk.
- EMI Shielding: They can work as an effective protection against electromagnetic interference. By enclosing sensitive components or traces within a copper pour, we can minimize the coupling of external electromagnetic fields and attenuate radiated emissions.
- Grounding Considerations: While copper pours can be effective, improper grounding or placement of copper pours can cause unintended consequences. If copper pours are not accurately attached to a solid ground plane or if there are discontinuities in the ground plane, it can cause unintended ground loops, increasing the chances of EMI issues.
- Parasitic Capacitance and Inductance: Copper pours can introduce parasitic capacitance and inductance to the board. This can impact signal integrity, causes signal degradation, and potential crosstalk issues. Accurate placement and configuration of copper pours, along with a controlled impedance design, can mitigate these factors
When and Why to Adopt a PCB Ground Pour?
Adopting a PCB ground pour, also called ground plane, can provide advantages and benefits in electronic circuit designs. Here are some conditions when and why you can select to use a PCB board ground pour:
- Signal Integrity: A ground pour can improve signal integrity by low-impedance return path for signals. It decreases the loop area of high-speed signal traces, reduces inductance, and reduces the chances of reflections, signal distortion, and crosstalk. A solid ground plane maintains a stable reference voltage, reduces ground bounce, and improves noise immunity.
- EMI/EMC Considerations: They can work as a protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and improve electromagnetic compatibility (EMC). By enclosing sensitive components and traces in a ground plane, it minimize the coupling of outer electromagnetic fields and attenuates radiated emissions.
- Power Distribution: it can facilitate effective power distribution throughout the board. Connecting power supply traces to the ground plane helps in maintaining a stable voltage reference and decreasing voltage loss. It also helps in heat dissipation, as the ground plane can work as a thermal conductor, spreading heat away from components.
- Controlled Impedance: They also help in getting controlled impedance for high-speed signal traces. By adjusting the width and placement of the ground pour in relation to signal traces, we can fine-tune the features impedance to match the required value. This helps in reducing signal reflections and maintaining signal integrity.
- RF and High-Frequency Designs: They are also effective in RF (Radio Frequency) and high-frequency designs. They offer a continuous ground reference, reducing parasitic capacitance and inductance, and reducing the chances of impedance mismatches.
Copper Pours vs Ground Pours
| Copper Pours | ||
|---|---|---|
| it offers a conductive area for copper traces or components | Signal Integrity | increases signal integrity by reducing inductance and noise |
| Canot provide significant EMI/EMC benefits | Power Distribution | Facilitate good power distribution and reduce voltage drops |
| impact impedance control for high-speed traces | RF and High-Frequency | beneficial for RF and high-frequency circuits |
| Not used designed for thermal management | Ground Reference | Offer a stable ground reference and reduce ground potential differences |
| offer more design flexibility and routing options | PCB Real Estate | Requires PCB real estate for the ground plane |
Importance of Copper Pour in Empty Areas on PCBs & Notes on Using Copper Pour
In a PCB design, too much-unused space without copper can have a detrimental impact on production and the caliber of the finished product. Filling empty space on a PCB board with planar copper is called placing copper pour. All significant PCB design software has the ability to automatically insert copper pour, which is an important component of PCB design. Copper pour decreases ground impedance, boosts power efficiency by minimizing voltage drops, and minimizes EMI by reducing loop regions, all of which contribute to the development of EMC.
JLCPCB produces high-quality PCBs in five independently owned intelligent manufacturing bases employing cutting-edge machinery and raw materials. All PCB manufacturing linkages are under the good control of JLCPCB.
Outer Layer copper pour: 2- and Multi-layer Boards
Boards are put in a plating solution and electroplated with a fixed current after a dry coating has been applied to them.
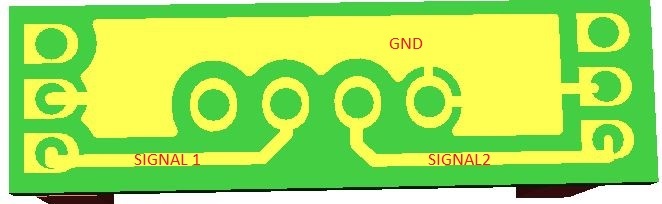
Discussions
Become a Hackaday.io Member
Create an account to leave a comment. Already have an account? Log In.